by Anton O. Tolman, Ph.D., Utah Valley University Guest Editor
There appears to be growing interest among faculty and researchers on the topic of metacognition. This is evidenced, in part, by increasing research and published works related to the subject such as Saundra and Stephanie McGuire’s (2015) book regarding teaching students how to learn. Other recent works (e.g., Doyle & Zakrajsek, 2018; Bain, 2012) are aimed primarily at students, encouraging them to recognize how the brain works and how they can adopt behaviors and strategies that will enhance their learning. These are laudable efforts that provide a solid foundation for faculty to introduce to students thereby increasing students’ chances of success. Yet, faculty and others who approach metacognition only from the perspective of enhancing student learning strategies or behaviors (process metacognition) are missing the opportunity for a deeper understanding of metacognition’s central role in learning.
With a broader understanding, all faculty and staff who have contact with students can promote and advocate for metacognitive skill development in general education, course development, across programs and curricula, and as valued skills in students’ personal and professional lives.
Three Ways Metacognition Can Enhance Student Success
Here are three quick examples of how metacognition furthers student success as well as promoting the overarching goals of colleges and universities:
- Fostering process metacognition helps students understand how they learn and promotes the acquisition and development of effective learning strategies across subjects (including General Education) as well as within the major. This promotes content mastery and improved academic skills and performance as well as transfer across knowledge domains, but only if the use of these skills is perceived as valued by instructors across courses and within the major. Otherwise, students tend to see this emphasis as restricted to a particular course or professor. If student advisors also encouraged buy-in of the value of these skills and their value to professional careers, this could also have a significant impact.
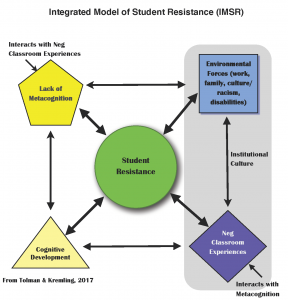
- Metacognition reduces student resistance to learning. Students, especially in their first years, often see themselves as consumers, functioning primarily in a passive “student” role they know well and are comfortable with. Resistance to learning is ubiquitous in education and plays a major role in decreasing student motivation to learn. Resistance arises due to systemic influences (see Tolman & Kremling, 2017), one of which is the lack of metacognitive awareness (see Figure below).
Students’ lack of self-awareness of learning strategies, their relative effectiveness, and the ability to monitor and evaluate their learning (beyond grades) naturally leads to negative classroom situations, frustration, and anxiety. In their consumer or “student” role, pushed in part by social expectations and institutional culture, many believe that if they have put in good effort, they should receive excellent grades. If this does not occur, natural targets of that frustration are the instructor (she doesn’t teach well), the content (I’m no good at this subject), or the generalization that they do not belong in college.
Promoting student metacognition, especially, shifts the responsibility for learning back towards the student who hopefully realizes they can succeed by using better learning approaches and encourages them to seek help when they realize they have not mastered important skills or concepts. This also increases student motivation and desire to learn and can curtail the sense that they do not belong. Instructors, advisors, and others who emphasize the relevance of metacognitive skills in professional careers, or even effective parenting, can help students see value and meaning in using these skills in many environments and across their lives.
- Another vital aspect of metacognition is that in becoming self-aware of their own motives, approaches, level of resistance, and personal responsibility, students begin to shift their personal narrative and identity away from that of consumer to that of someone capable of success. They begin to see themselves as someone who can be a lifelong learner and a learned person in their profession and in society. Taraban (2020; Taraban & Blanton 2008) described this process of personal narrative development as inherently metacognitive. In addition, Hale (2012) likewise explores the powerful interdependent relationships between metacognition, critical thinking, and personal narrative.
These relationships are so interdependent and so potent, they underlie the documented effectiveness of what are called “high impact practices” in learning and retention. A good example of this is the power of undergraduate research, an enterprise heavily laden with metacognitive experiences if done well, to shape students’ personal narratives and create a new sense of identity as a scholar, as someone capable of asking their own questions and finding answers. These experiences are especially powerful for first-generation and minority students as clearly described by Charity Hudley, Dickter, and Franz (2017) and the work of Tarabon and Blanton (2008).
Overview of this Guest Editor Series
Even with these limited examples, it should become obvious that metacognition is central to successful learning. The purpose or goal of this Mini-series is to explore several pivotal aspects of learning in higher education related to student resistance and motivation and to encourage all faculty and students to explore these boundaries. In the upcoming blogs, you will hear from the following authors on several important subjects:
- Christopher Lee on How Metacognition Can Facilitate Student Inclusion in the Classroom
- Steven Pearlman on Metacognition and the Fish in the Water
- Benjamin Johnson on Change Instead of Continuity: Using Metacognition to Enhance Student Motivation for Learning
- Anton Tolman on Boosting the Effectiveness of Collaborative Learning Using Metacognition
I will conclude the series with a blog focusing primarily on personal narrative and self-identity. Above, I noted that student resistance is a common occurrence in our classrooms. However, resistance is not limited to students. It is time that we, as professors, go beyond the constraints of thinking of ourselves as “content experts” and consider the broader scope of what we are capable of achieving by promoting metacognition in our assignments, our curriculum, across the major, and our institutions. We hope this blog series will help you see some new possibilities.
References
Bain, K. (2012). What the Best College Students Do. Belknap Press.
Charity Hudley, A.H., Dickter, C.L., & Franz, H.A. (2017). The Indispensable Guide to Undergraduate Research: Success In and Beyond College. New York: Teachers College Press.
Doyle, T. & Zakrajsek, T.D. (2018). The New Science of Learning: How to Learn in Harmony with Your Brain (2nd Ed). Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing.
McGuire, S. Y. & McGuire, S. (2015). Teach Students How to Learn: Strategies You Can Incorporate Into Any Course to Improve Student Metacognition, Study Skills, and Motivation. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing.
Taraban, R., & Blanton, R. L. (Eds.). (2008). Creating Effective Undergraduate Research Programs in Science: The Transformation from Student to Scientist. New York: Teachers College Press.
Taraban, R. (2020, June 25). Metacognition and the Development of Self. ImproveWithMetacognition.com. https://www.improvewithmetacognition.com/metacognition-and-self-identity/
Tolman, A.O. & Kremling, J. (2017). Why Students Resist Learning: A Practical Model for Understanding and Helping Students. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing.