by Anton Tolman, PhD, Guest Editor, Utah Valley University
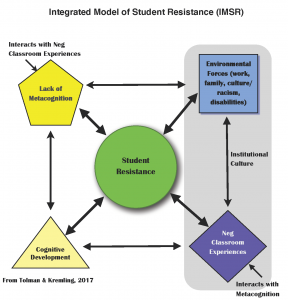
The introductory blog for this series included a figure of the Integrated Model of Student Resistance (IMSR; Tolman & Kremling, 2017). That image (shown below) illustrates that student resistance is the outcome of systemic factors, including lack of metacognition. The IMSR demonstrates that family and the larger culture (including institutional culture) may promote consumer expectations and that these elements (poor metacognitive skills and culture) often intersect with instructor behaviors and attitudes, leading to negative experiences in education. This, in turn, increases student resistance, especially towards active learning.
These elements are also exacerbated by student cognitive development, which is overlooked by many instructors as a relevant element in metacognition, classroom experiences, and resistance. For example, Nufher (2014) summarizes the work of William Perry (1999) who carried out longitudinal studies of college student cognitive development. Students react with varying degrees of resistance to education depending on their level of cognitive development. Progressing in cognitive development can take time, but several authors have noted that effective use of metacognition and other strategies may accelerate this process, including careful metacognitive exercises (see Nuhfer, 2014; Nelson, 2015; Kloss, 1994).
The IMSR was created to help instructors begin to see resistance differently than they typically do; it is a communication signal from students that something is not working and, rather than dismiss it or try to assert their authority, the solution lies in addressing the underlying causes, including lack of metacognition. A recently published study in nursing (Stover & Holland, 2018) reported that use of the IMSR to redesign a collaborative learning-based course resulted in reduced resistance to collaborative learning, a greater sense of belonging to a community of inquiry, higher student satisfaction, and less negative comments or concerns. For a full explanation of the model, see Tolman and Kremling (2017).
Students not actively using metacognitive skills are more likely to resist active teaching efforts because they see themselves as passive consumers of information whose main concern is to meet requirements set by an authority figure in order to graduate. My experience is that student resistance is greater in courses requiring collaborative learning because students are expected to work together on activities important to their grade. Now, imagine the level of resistance to collaborative learning in my online Abnormal Psychology course! When students see the syllabus, the most common resistant comment I receive is “I took this course online so I would not have to work with others.”
We should acknowledge that some of that resistance is justified. Collaborative learning pedagogies are not simple, and unfortunately are sometimes implemented ineffectively, leading to negative experiences for students. U.S. culture is highly individualistic and emphasizes personal success rather than group efforts despite the fact that society depends on the ability of people to work effectively together. Students often see collaborative learning as either a potential threat to their grade, or often based on prior experiences, as an added burden due to social loafing by peers. Many students have never been explicitly taught how to manage conflict, work with others, seek understanding of alternate viewpoints, and are unaware of the data indicating that diverse groups usually reach more effective problem solutions.
Thus, we have a storm of interacting elements here of culture/consumerism, negative prior experiences (with both peers and instructors), student lack of awareness of their own level of communication and collaboration skills and how to monitor and improve collaboration, and usually cognitive development where some students on the team see collaborative assignments as about “getting the right answer” rather than being about enriching their understanding of the material and promoting critical thinking (see Nelson, 2015). Let’s use the specific example of my Abnormal Psychology course to illustrate these issues and how promoting metacognition can help.
Example of Incorporating Metacognition: An Online Abnormal Psychology Course
Students know from the syllabus that the class will involve working in teams; they also know that course objectives are weighted towards development of professional skills as well as content learning. They begin to engage with metacognitive assignments by completing two instruments1:
- the TTM-Learning Survey (TTM-LS) assesses the student’s degree of readiness to change how they learn and their readiness to engage with a collaborative team, and
- the Learning Strategies Self-Assessment (LSSA) measures how often they use known effective learning strategies and engages them with reflective questions.
These assignments are due the first two weeks, before team activities begin.
A comparison of typical responses across two particular LSSA questions reveals some helpful insights on student thinking about collaborative learning. One LSSA reflective question asks them about their personal goals for the course. Despite knowing the class will involve teamwork, only 5% of the students indicated any related personal goal for improving their teamwork skills and learning (Fall, 2018 class). However, when the LSSA asks students to review their learning strategy scores and identify their strengths and weaknesses as a learner, 39% of them acknowledged weakness in collaboration or a reluctance to work with others. For instance,
- Student A wrote, “I have a hard time asking for help when I get frustrated or confused. I feel like it is my responsibility to learn the material and do not want to put someone else out by making them take the time to teach me a concept I should be able to learn on my own.”
- Student B replied, “I noticed that I’m very good at doing things on my own but when it comes to asking for help or working in groups, I don’t do it as often.”
- Student C said, “I have learned many strategies throughout my academic experience on working with teams and they were mostly negative.”
At the beginning of the semester, these instruments opened the door for students to own these emotions and experiences, to think about how they could do better, how ready they were to change, to take responsibility for their own skill development, and to at least be willing to consider the value of collaborative learning. Instructors using instruments like this have the opportunity to provide feedback, lower resistance, and engage with these students in productive ways to prepare them to do well in a collaborative course, even if it is online.
Sibley and Ostafichuk (2014) describe some interventions instructors can take to help students “buy in” to the value of Team-Based Learning (TBL) including explaining the purpose and relevance of TBL, acknowledging negative experiences, and demonstrating the difference in quiz scores by teams compared with individuals (teams do better). These efforts are useful, but they are not inherently metacognitive and could be seen as just more instructor justification. The critical task for the instructor is to foster, across the semester, metacognitive thinking and evaluation of how collaborative experiences enhance their learning and strengthen their critical thinking and communication skills. Other aspects of TBL such as self and peer evaluation, if done well, also promote metacognitive development and learning.
Making Metacognition Pervasive
To be effective, metacognitive activities in collaborative environments must occur across the semester; single assignments or events will be insufficient. For example, a week after completing the two instruments above, students complete a Personal Learning Plan. They are asked to reflect on their TTM-LS readiness to change stages and to explain their next steps to become more effective learners and team members. They also create a personal study plan for the semester.
As students launch their teams, they engage in readings about the value of professional team skills in the workplace and engage with sites like Surviving the Zombie Apocalypse (https://teamwork.umn.edu/) to identify common myths contributing to negative experiences and devise a plan for working together. A later team workshop asks them to evaluate team progress and identify areas for improvement. Online videos and class discussions on these topics, connecting the themes to professional practice in the field, are also vital. These metacognitive “boosters” help them continue progress in the development of these skills.
Wirth and Perkins (2013) note that metacognitive skills must be developed in the disciplinary context, with students questioning their own mastery, progress, and applying relevant concepts. Designing collaborative learning courses to engage students in metacognitive activities from the very beginning and then continuing that dialogue can lead to significant gains in learning content and development of metacognitive, critical thinking, and collaboration skills.
At the end of the semester, my students complete the TTM-LS and LSSA again. Some questions ask them to identify activities that enriched their learning and how they will use what they learned in the future.
- Student A stated, “I will try to form a study group or a team to try to learn the material, because I felt the more I taught the others the more I learned for myself.”
- Student B noted, “…Meeting in a group was probably the most beneficial way for me to learn the course material. Looking back, it’s kind of ironic that that is my favorite aspect because I fought it so hard in the beginning”, and
- Student C, who had a difficult semester, reflected, “[My] attitudes have been changing and so [has]my way of dealing with group work. I learned I had to change my attitude in order to change the way I think about an issue…”
In total, 80% of the students made statements positive about team work and how it benefitted them in response to these questions. Building ongoing metacognitive activities into collaborative learning environments makes a significant difference to student success.
References
Kloss, R.J. (1994). A nudge is best. College Teaching, 42(4), 151-159.
Nelson, C. (2015, February 15). Fostering Metacognition: Right-Answer Focused versus Epistemologically Transgressive. ImprovewithMetacognition.com. https://www.improvewithmetacognition.com/fostering-metacognition-right-answer-focused-versus-epistemologically-transgressive/
Nuhfer, E. (2014, July 15). Metacognition for Guiding Students to Awareness of Higher-level Thinking (Part 1). ImprovewithMetacognition.com. https://www.improvewithmetacognition.com/metacognition-for-guiding-students-to-awareness-of-higher-level-thinking-part-1/
Perry, W. G., Jr. (1999). Forms of intellectual and Ethical Development in the College Years. (Reprint of the original 1968 1st ed). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Sibley, J. & Ostafichuck, P. (Eds). (2014). Getting Started with Team-Based Learning. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing.
Stover, S. & Holland, C. (2018). Student resistance to collaborative learning. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 12(2), Article 8. https://doi.org/10.20429/ijsotl.2018.120208
Tolman, A.O. & Kremling, J. (2017). Why Students Resist Learning: A Practical Model for Understanding and Helping Students. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing.
Wirth, K.R. & Perkins, D. (2008). Learning to Learn. Retrieved from: http://www.macalester.edu/geology/wirth/CourseMaterials.html
1 These instruments are available under a Creative Commons license, so feel free to contact me (Anton Tolman).